
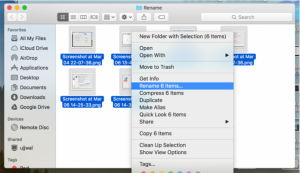
The purpose of special argument -, which is supported by most utilities, is to signal that subsequent arguments should be treated as operands (values), even if they look like options due to starting with -, as Jacob C. Similar to the bash solution, s/././ performs text substitution, but - unlike in bash - true regular expressions are used.Here's the equivalent of the command at the top using rename: rename -n -e 's/_.*_/_/' *.pngĪgain, this command performs a dry run remove -n to perform actual renaming. On macOS you can install it using popular package manager Homebrew as follows: brew install rename If you find yourself batch-renaming files frequently, consider installing a specialized tool such as the Perl-based rename utility.
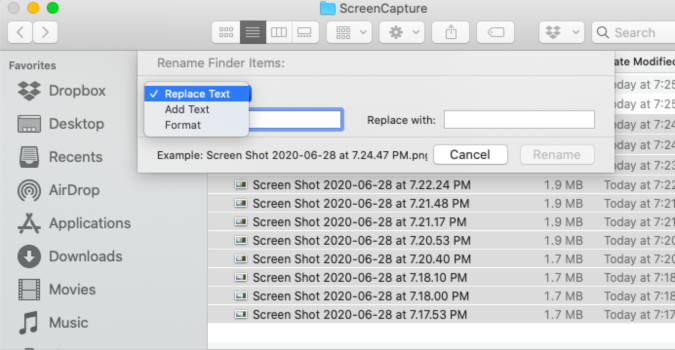
Note that _*_ is a pattern (a wildcard expression, as also used for globbing), not a regular expression (to learn about patterns, run man bash and search for Pattern Matching).
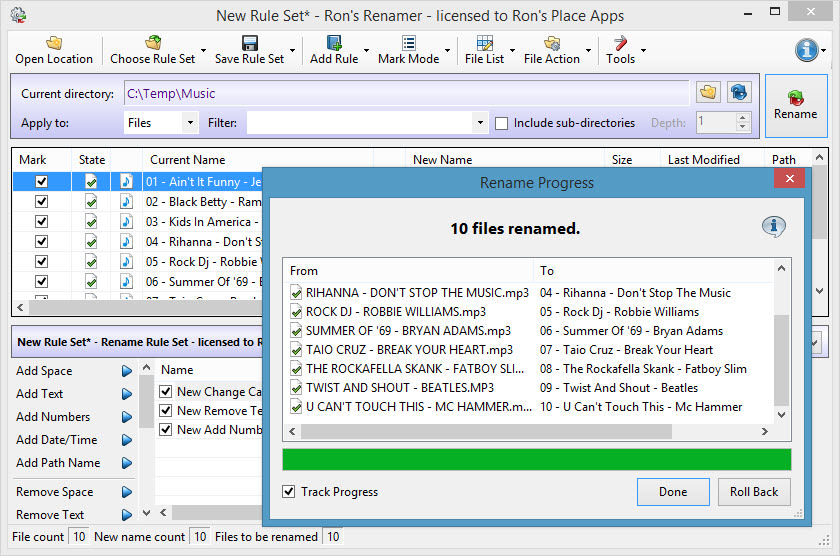
In your specific case you can use the following bash command ( bash is the default shell on macOS): for f in *.png do echo mv "$f" "$" is an application of bash parameter expansion: the (first) substring matching pattern _*_ is replaced with literal _, effectively cutting the middle token from the name.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
